On what surfaces can it be used
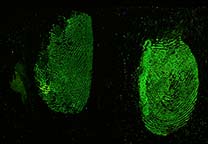
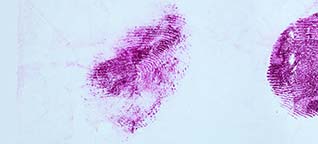
Acid Yellow 7 is a dye solution in a water/acetic acid/ethanol mixture that is used for staining fingerprints and shoeprints made in blood [1]. Prints in blood are colored yellow after treatment with Acid Yellow 7. They then fluoresce under blue/blue-green light. Acid Yellow 7 should not be used on absorbent surfaces like paper, carton material, bed sheets, or carpet. It works very well on non-absorbent backgrounds like linoleum, glass, tiles, painted surfaces, or PVC floor covering.
Before staining, prints in blood should be fixed to prevent them from running (causing loss of detail) when the staining solution is applied. In general fixative is applied before any staining solution except Leuco Crystal Violet, which contains fixative.
How to fix the prints
Fixing is best done with a 2% solution of sulfosalicylic acid in water (20-23 gram in 1 liter). To make sure the print in blood is thoroughly fixed, we recommended the following method using absorbent paper (like filter paper, tissue paper, or paper towels) and a wash bottle containing sulfosalicylic acid solution.
Take a dry piece of the absorbent paper that is sized to cover the print(s). Hold it directly over the print-area, parallel to the surface and just slightly above the surface. To begin fixing, drop one edge of the paper to the surface and moisten heavily along its entire length, so that it is anchored and will stay in place.
Starting from that edge, wet the paper progressively further while smoothing the wetted part onto the print and minimizing trapped air bubbles. Work carefully from one edge to the other. When possible, for example, with an object or with a print on an angled surface start from the top and work downwards.
Once the wet paper entirely covers the print, leave it there for a minimum of three minutes.When the blood is a thick layer, leave the paper there 5 minutes or more. Remove the paper. An excess of fixative can be rinsed away with water, but this is not necessary.
When the blood is relatively fresh, you will notice that fixing changes its color from dark red to dark brown.
Staining procedure
Once the print is fixed, it can be stained with Acid Yellow 7 solution. Use a wash bottle to apply the solution to the article or area of interest. With fingerprints, a disposable pipet can be used. Alternatively you can submerge the article in a container/bath of solution if the size of the article permits.
Spraying is technically feasible but will likely raise the amount of ethanol vapor in the air. Sufficient protection measures should be taken to avoid inhalation of aerosols.
After the staining solution is applied leave it in contact with the print for 1-3 minutes. Then wash the surface with the same water/acetic acid/ethanol mixture as used for the dye solution, but without the dye.
Alternatively, water can be used but may result in more background staining. If the print is located on a floor, the wash solution might be removed with a vacuum cleaner that can handle water. Otherwise, remove it with paper towels or the like.
Lifting and fluorescence
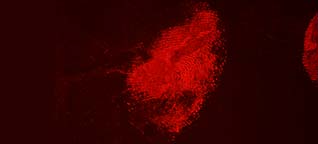
Acid Yellow 7 not only has a good staining capacity but has some special characteristics.The stained prints will fluoresce when excited with blue and blue-green light though the fluorescence will be faint. To obtain the best result, eliminating backgrounds and/or background fluorescence, stained prints can be lifted with a white BVDA Gellifter.
Before lifting with the white Gellifter, the area should be completely dry. Be very careful not to trap air bubbles under the lifter surface. Leave the lifter on the print for only a short time, something like a minute. Photograph within a couple of hours after lifting as the dye will slowly diffuse in and across the surface of the lifter, thereby blurring the print.
Lifting can be done more than once, with or without re-staining between lifts. Repeat lifting/staining in important cases.
Fluorescence is excited with blue and blue-green light (400-490 nm) and visible even when using long-wave UV. The filter used in front of the lens depends on the excitation wavelength: clear for UV to yellow/light orange for the higher wavelengths.
Safety
Acid Yellow 7 powder is not labeled as a hazardous preparation. Since its working solution is based on a water/ethanol mixture, no harmful fumes are liberated in normal use, although the acetic acid smell might be irritating. When large amounts are used and/or the temperature is high enough, a potentially explosive air/ethanol vapor mixture can result unless ample ventilation is provided. Acid Yellow 7 solution will color the skin and clothing.
Sulfosalicylic acid crystals are labeled as an irritant substance but the 2% solution is not labeled as a hazardous product. Given the fixative effect on blood, we strongly advise wearing gloves (vinyl gloves will suffice) when using it.
Avoid breathing aerosols (mists) and vapors of the fixative, washing liquid, and Acid Yellow 7 solution. Likewise avoid contact with solutions and the Acid Yellow 7 powder. Wash your hands after each session, especially before eating or drinking.
Composition of the solutions
Acid Yellow 7
| 1 gram | Acid Yellow 7 |
| 50 ml | acetic acid (glacial, 99%) |
| 250 ml | ethanol (98% or higher) |
| 700 ml | demineralized or distilled water |
| -------- | |
| 1000 ml | working solution |
Preferably use an Erlenmeyer flask for preparation of the Acid Yellow 7 solution. Add water first and dissolve the Acid Yellow 7 powder in the water by swirling the flask or using a magnetic stirrer and a PTFE-covered stir bar. The powder will dissolve quickly. Then add ethanol and acetic acid (order not important.)
Blood fixative
| 20 grams | 5-Sulfosalicylic acid, dihydrate |
| 1000 ml | demineralized or distilled water |
| -------- | |
| 1000 ml | working solution |
Add components to a beaker/flask of suffient size and mix till complete dissolution, using a magnetic stirrer.
Washing solution
| 50 ml | acetic acid (glacial, 99%) |
| 250 ml | ethanol (98% or higher) |
| 700 ml | demineralized or distilled water |
| -------- | |
| 1000 ml | washing solution |
References and footnotes
[1] Sears, V.G.; Butcher, C.P.G.; Fitzgerald, L.A. "Enhancement of Fingerprints in Blood, Part 3: Reactive Techniques, Acid Yellow 7, and Process Sequences." Journal of Forensic Identification 2005, Vol. 55, No. 6, p. 741-763.
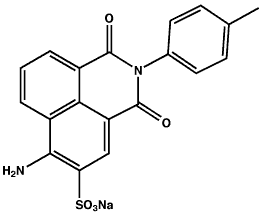
Name: Acid Yellow 7 (CI 56205), 6-Amino-2,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-2-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-benz[de]isoquinoline-5-sulfonic acid sodium salt
CAS No.: 2391-30-2